Factor A has K levels k 1 K Factor B has J levels j 1 J. G a b treatments altogether where the treatments are the combinations of the levels of the two factors. A two way anova means that the experimental design includes.
A Two Way Anova Means That The Experimental Design Includes, To begin withlet us define a factorial experiment. Two grouping variables we sometimes refer to the analysis as a two-way ANOVA in contrast to the one-way ANOVAs that we ran in Chapter 12. Two factor twoway ANOVA Twofactor ANOVA is used when. In the two-way ANOVA model there are two factors each with several levels.
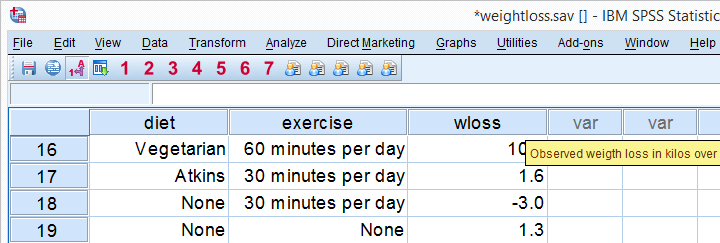 Spss Two Way Anova Quick Tutorial From spss-tutorials.com
Spss Two Way Anova Quick Tutorial From spss-tutorials.com
Two variables are said to interact when. Thinking again of our walruses researchers might use a two-way ANOVA if their question is. Revised on January 7 2021. G a b treatments altogether where the treatments are the combinations of the levels of the two factors.
A two-way ANOVA is an extension of the one-way ANOVA analysis of variances that reveals the results of two independent variables on a dependent variable.
Read another article:
In a matrix for a factorial design the row means and column means represent the effects of a singe factor variable. Completely randomized design with treatments randomly assigned to the g. Subsequently question is what is in an experimental design. If an experiment has a quantitative outcome and two categorical explanatory variables that are de ned in such a way that each experimental unit subject can be exposed to any combination of one level of one explanatory variable and one. In the two-way ANOVA model there are two factors each with several levels.
 Source: technologynetworks.com
Source: technologynetworks.com
Published on March 20 2020 by Rebecca Bevans. Model for the two-way factorial experiment. In one-way ANOVA we classify populations according to one categorical variable or factor. A two-way ANOVA is like a one-way ANOVA a hypothesis-based test. One Way Vs Two Way Anova Differences Assumptions And Hypotheses Technology Networks.
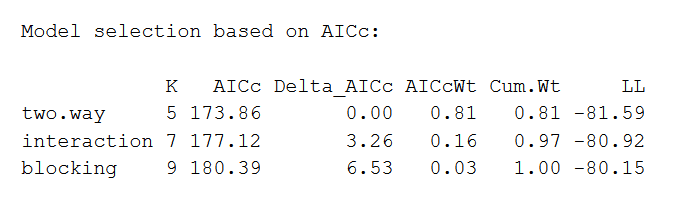 Source: scribbr.com
Source: scribbr.com
Level of a factor p. Balanced Design Two factors. In the two-way ANOVA model there are two factors each with several levels. Emphasis will be placed on important design-related concepts such as randomization blocking factorial design and causality. Two Way Anova When And How To Use It With Examples.
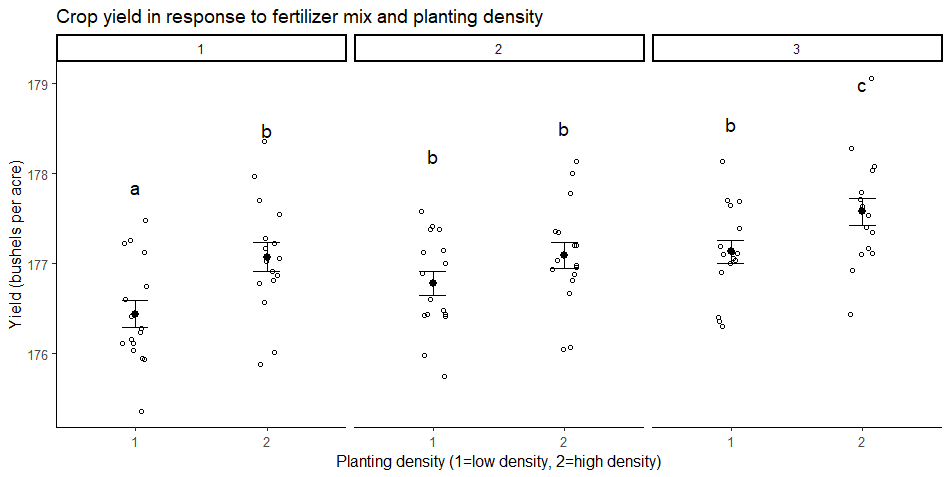 Source: scribbr.com
Source: scribbr.com
One or More Independent Variables With Two or More Levels Each and More Than One Dependent Variable. Two variables are said to interact when. ANOVA and ANCOVA presented as a type of linear regression model will provide the mathematical basis for designing experiments for data science applications. Revised on January 7 2021. Two Way Anova When And How To Use It With Examples.
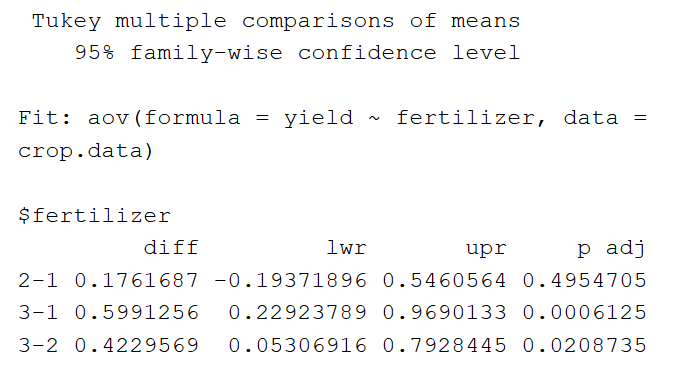 Source: scribbr.com
Source: scribbr.com
As in one-way ANOVA the data for a two-way ANOVA study can be experimental or observational. The difference between one-way and two-way ANOVA is that in two-way ANOVA the effects of two factors on a response variable are of interest. A two-way ANOVA is like a one-way ANOVA a hypothesis-based test. Y is a quantitative response variable There are two categorical explanatory variables called Factors. One Way Anova When And How To Use It With Examples.
 Source: scribbr.com
Source: scribbr.com
Balanced Design Two factors. To perform two-way ANOVA for an unbalanced design use anovan. A two-way ANOVA is like a one-way ANOVA a hypothesis-based test. One or More Independent Variables With Two or More Levels Each and More Than One Dependent Variable. A Quick Guide To Experimental Design 5 Steps Examples.
 Source: dzchilds.github.io
Source: dzchilds.github.io
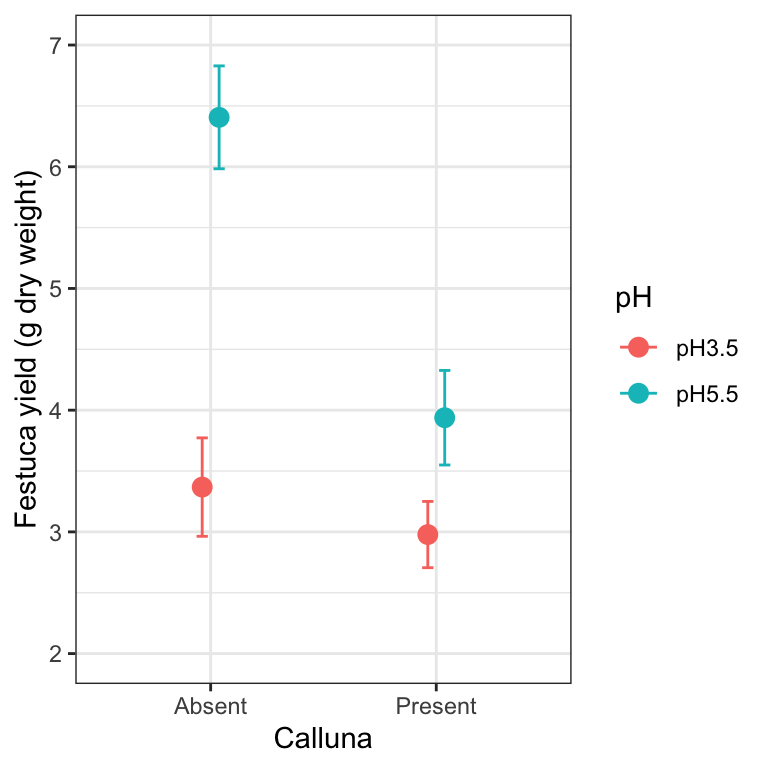
Two grouping variables we sometimes refer to the analysis as a two-way ANOVA in contrast to the one-way ANOVAs that we ran in Chapter 12. Revised on January 7 2021. Subsequently question is what is in an experimental design. In the two-way ANOVA model there are two factors each with several levels. Chapter 27 Two Way Anova In R Aps 240 Data Analysis And Statistics With R.
 Source: statistics.laerd.com
Source: statistics.laerd.com
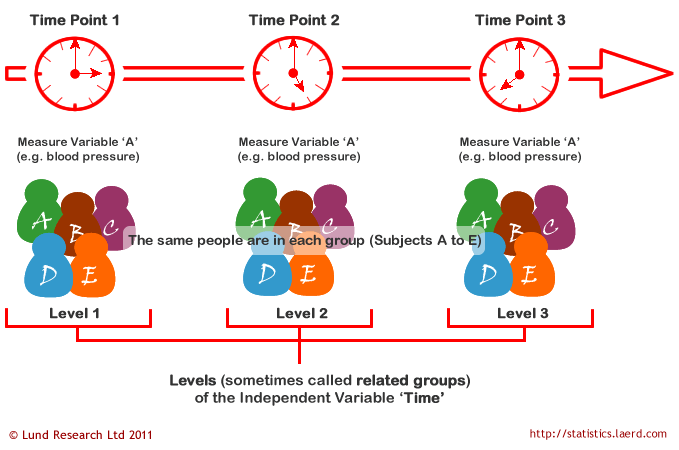
Factor A has K levels k 1 K Factor B has J levels j 1 J. If an experiment has a quantitative outcome and two categorical explanatory variables that are de ned in such a way that each experimental unit subject can be exposed to any combination of one level of one explanatory variable and one. Model for the two-way factorial experiment. Two-Way ANOVA An analysis method for a quantitative outcome and two categorical explanatory variables. Repeated Measures Anova Understanding A Repeated Measures Anova Laerd Statistics.
 Source: scribbr.com
Source: scribbr.com
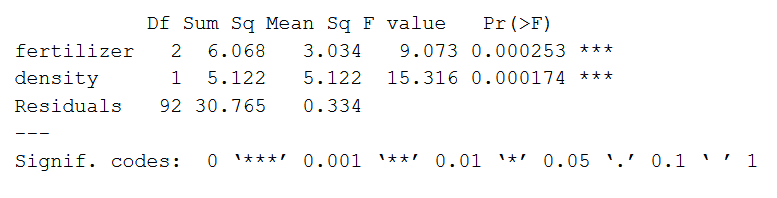
The difference between one-way and two-way ANOVA is that in two-way ANOVA the effects of two factors on a response variable are of interest. If the model has two categorical factors it is a two-way ANOVA. Two-Way ANOVA An analysis method for a quantitative outcome and two categorical explanatory variables. If an experiment has a quantitative outcome and two categorical explanatory variables that are de ned in such a way that each experimental unit subject can be exposed to any combination of one level of one explanatory variable and one. Two Way Anova When And How To Use It With Examples.
 Source: dzchilds.github.io
Source: dzchilds.github.io
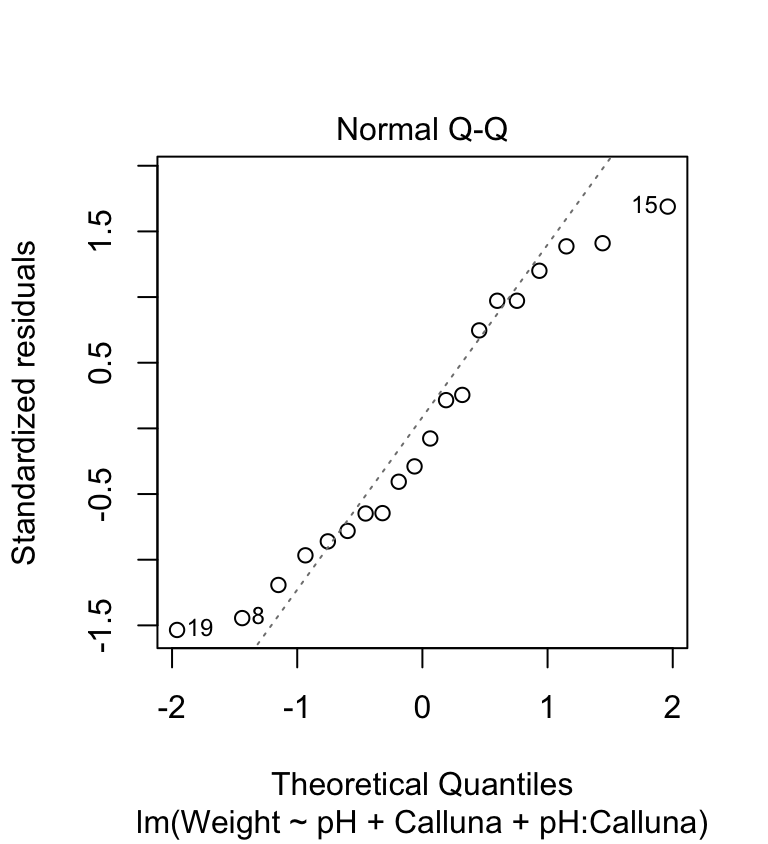
In one-way ANOVA we classify populations according to one categorical variable or factor. Balanced Design Two factors. To perform two-way ANOVA for an unbalanced design use anovan. However in the two-way ANOVA each sample is defined in two ways and resultingly put into two categorical groups. Chapter 27 Two Way Anova In R Aps 240 Data Analysis And Statistics With R.
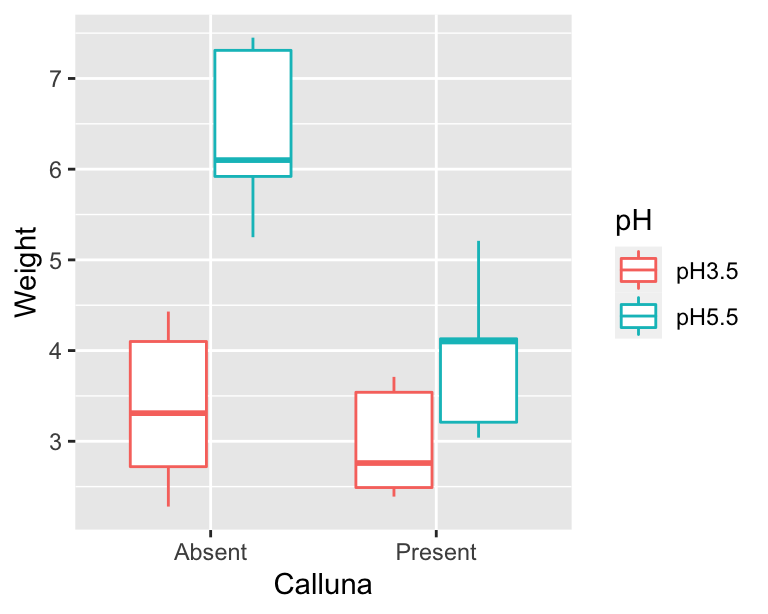 Source: dzchilds.github.io
Source: dzchilds.github.io
Experimental design refers to how participants are allocated to the different conditions or IV levels in an experiment. As in one-way ANOVA the data for a two-way ANOVA study can be experimental or observational. 131 Factorial ANOVA 1. Y is a quantitative response variable There are two categorical explanatory variables called Factors. Chapter 27 Two Way Anova In R Aps 240 Data Analysis And Statistics With R.
 Source: keydifferences.com
Source: keydifferences.com
One or More Independent Variables With Two or More Levels Each and More Than One Dependent Variable. Model for the two-way factorial experiment. For an example see Two-Way ANOVA for Unbalanced Design. Subsequently question is what is in an experimental design. Difference Between One Way And Two Way Anova With Comparison Chart Key Differences.
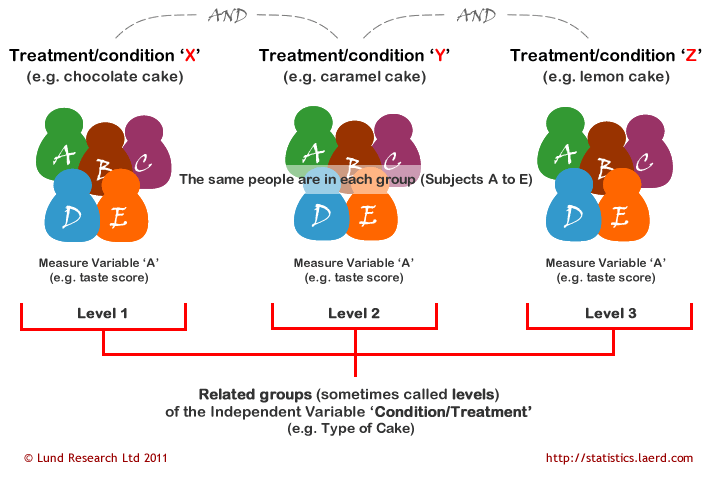 Source: statistics.laerd.com
Source: statistics.laerd.com
Emphasis will be placed on important design-related concepts such as randomization blocking factorial design and causality. Level of a factor p. Balanced Design Two factors. 131 Factorial ANOVA 1. Repeated Measures Anova Understanding A Repeated Measures Anova Laerd Statistics.
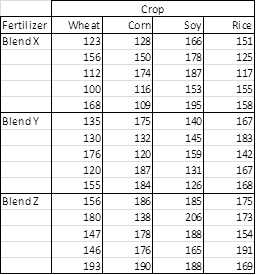 Source: real-statistics.com
Source: real-statistics.com
A two factor experiment means that the experimental design includes. If the model has a single categorical factor and one continuous factor it is an ANCOVA short for analysis of covariance next chapter. Balanced designs no interactions When we discussed analysis of variance in Chapter 12 we assumed a fairly simple experimental design. The difference between one-way and two-way ANOVA is that in two-way ANOVA the effects of two factors on a response variable are of interest. Two Way Anova W Replication Real Statistics Using Excel.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
ANOVA and ANCOVA presented as a type of linear regression model will provide the mathematical basis for designing experiments for data science applications. If the model has a single categorical factor and one continuous factor it is an ANCOVA short for analysis of covariance next chapter. If the model has two categorical factors it is a two-way ANOVA. A two-way ANOVA is an extension of the one-way ANOVA analysis of variances that reveals the results of two independent variables on a dependent variable. Detailed And Helpful Compare Contrast Between Other Methods Cause And Effect What Is Meant Compare And Contrast.
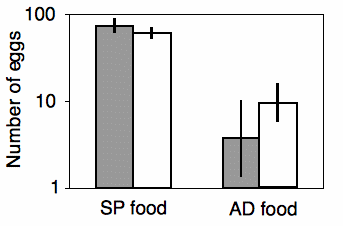 Source: biostathandbook.com
Source: biostathandbook.com
Balanced designs no interactions When we discussed analysis of variance in Chapter 12 we assumed a fairly simple experimental design. In the two-way ANOVA model there are two factors each with several levels. The two-way ANOVA is probably the most popular layout in theDesign of Experiments. The designing of the experiment and the analysis of obtained data are inseparable. Two Way Anova Handbook Of Biological Statistics.







